Please Re Import the Gradle Project and Try Again
Gradle projects
IntelliJ IDEA lets yous manage Gradle projects. Y'all tin can link, ignore projects, work with profiles, and synchronize changes in Gradle and IntelliJ Thought projects. You tin can too configure a Gradle composite build, Gradle source sets, the build and run deportment.
Navigate to the build.gradle file
-
In the Gradle tool window, right-click a linked projection.
-
From the context menu, select Open Gradle config F4.
IntelliJ Thought navigates to the advisable Gradle configuration file and the related build.gradle file opens in the editor.
Navigate inside a multi-module projection
IntelliJ IDEA supports a navigation to subprojects inside the parent build script of a multi-module Gradle project.
-
Open up build.gradle of the parent project.
-
Apply the Ctrl+Click shortcut to navigate to a subproject.

You can likewise come across the usages of a subprojects with the Alt+F7 and check the results in the Find tool window.

Unlink a linked Gradle project
When you lot unlink a Gradle project, IntelliJ Idea removes all relevant modules and content roots, removes the Gradle projection from the Gradle tool window and stops its synchronization. It might be helpful if y'all need to fully remove the previously linked Gradle project from the current IntelliJ IDEA project.
-
In the Gradle tool window, right-click a linked project.
-
From the context menu, select Unlink Gradle project (Delete). Alternatively, you tin select the linked project and click
on the tool window'south toolbar.
-
In the Import Gradle Projects popup, clear the checkbox confronting the modules if you don't want to delete the projection from the IntelliJ Idea Project tool window.
-
Click OK.
If you need to link back the project, in the Projection tool window, right-click the project'south build.gradle file or build.gradle.kts if it is a Kotlin project, and select Import Gradle Project.
Ignore a Gradle project
You can de-activate a Gradle project using the Ignore Gradle Projection option. In this instance, IntelliJ Thought keeps the ignored Gradle projects and subprojects in the Gradle tool window, merely stops their import (modules, content roots, tasks, then on) to the project. Withal, IntelliJ Thought synchronizes the ignored projects with the current one. Information technology might be helpful if you lot need to skip an irrelevant subproject such as buildSrc.
-
In the Gradle tool window, correct-click the project that you desire to ignore.
-
From the context menu, select Ignore Gradle Project.
-
In the window that opens, select projects and modules that you desire to de-activate and click OK.
If y'all want to activate your Gradle projects or modules, select Unignore Gradle Projects from the context carte du jour.
Orphan modules
Orphan modules are the IDE modules that were removed during the import process in the following cases:
-
when you lot manually deleted the modules in the build.gradle file and so re-imported your project.
-
when you lot used the Ignore Projection activity, on a module in the Gradle tool window and and so re-imported your project.
In all these cases, IntelliJ IDEA prompts you to restore removed modules.

Yous can select the ones you want to restore in the Orphan Modules dialog.
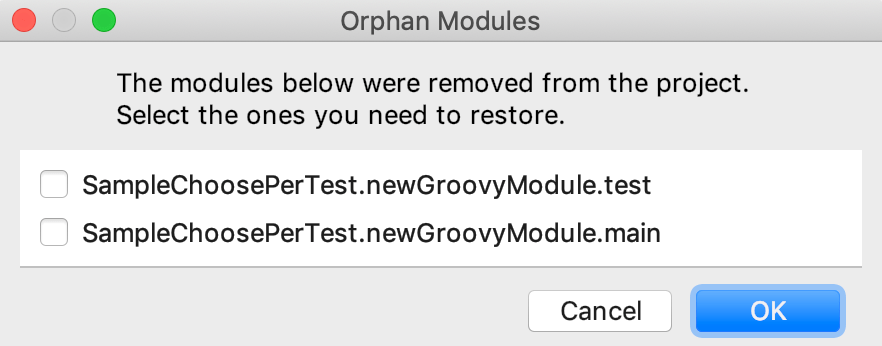
Usually you practise not need to restore whatsoever modules since these are only the .iml files that contain the IDE modules settings. You lot only might desire to restore them if you have some user-defined settings specified within them.
Reload a linked Gradle projection
When you open up a Gradle project the synchronization is done automatically. Also, when IntelliJ IDEA detects any external changes to the build scripts, such as VCS updates or some edits fabricated outside of the IDE, the related projects will exist reloaded automatically.
If you lot need, you can manually trigger the synchronization of your project.
-
In the Gradle tool window, right-click a linked project.
-
From the context menu, select Reload Gradle project
.
On invoking this action, IntelliJ IDEA parses the project construction in the Gradle tool window.
IntelliJ Thought cannot reload just a part of your projection, it reloads the whole project including modules and dependencies.
If you configure a dependency through the Project Structure dialog (click
, from the primary menu), the dependency will simply announced in the IntelliJ Idea Project tool window, not in the Gradle tool window. Notation that the next time you re-import your project, IntelliJ IDEA will remove the added dependency since IntelliJ IDEA considers the Gradle configuration every bit a single source of truth.
-
Click
on the condition bar to view the results of the sync in the Build tool window.
Configure the automobile-reload
-
In the Settings/Preferences dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S), become to .
Alternatively, In the Gradle tool window, click
and select the Auto-Reload Settings selection.

-
In the Build tools settings, specify the post-obit options:

-
Reload changes in the build scripts: this option is selected by default. If you want to disable the auto-reload and manually command the reloading process, unselect this checkbox.
-
Any changes: select this selection if you want to automatically reload the project later on any changes you make to build.gradle or external changes.
Every time you lot manually change the Gradle build script in the editor, you need to load the changes. IntelliJ IDEA displays a notification icon in the right part of the editor suggesting to Load Gradle Changes made to the project (Ctrl+Shift+O).

With the Any changes selection, IntelliJ Thought reloads all the changes automatically.
-
External chages: when you select this choice, IntelliJ Thought automatically reloads the project but after the VCS changes and changes made to the build files exterior the IDE.
-
Configure Gradle Blended Build
Before you start configuring your composite build, make sure you have the Gradle version iii.1 or later configured for your project.
You can employ the settings.gradle file to include Gradle builds for your Gradle composite build.
-
Open the settings.gradle file in the editor.
-
Using the
includeBuildcommand, specify the location of the builds you desire to add as dependencies to your project.
You tin also use the Gradle tool window to configure the composite build.
-
Open a Gradle projection.
-
Link other Gradle projects that you want to use for the composite build.
-
In the Gradle tool window, correct-click your chief project and from the context menu select Composite Build Configuration.
-
In the Gradle Projection Build Blended dialog, select projects that yous desire to include in your Gradle composite build.
-
Re-import your main Gradle project.
IntelliJ IDEA finds the included Gradle projects and treats them as IntelliJ Thought modules.
Use Gradle source sets
IntelliJ IDEA lets you use Gradle source sets in resolving Gradle projects. The source prepare is treated as a module in an IntelliJ IDEA project. You can declare a custom source set and IntelliJ IDEA adds information technology as a module to the project.
When you create a Gradle project, IntelliJ Thought automatically creates a main Source Sets directory that contains two source sets - chief and exam. IntelliJ IDEA also displays compile and runtime configurations in the Dependencies node in the Gradle tool window.
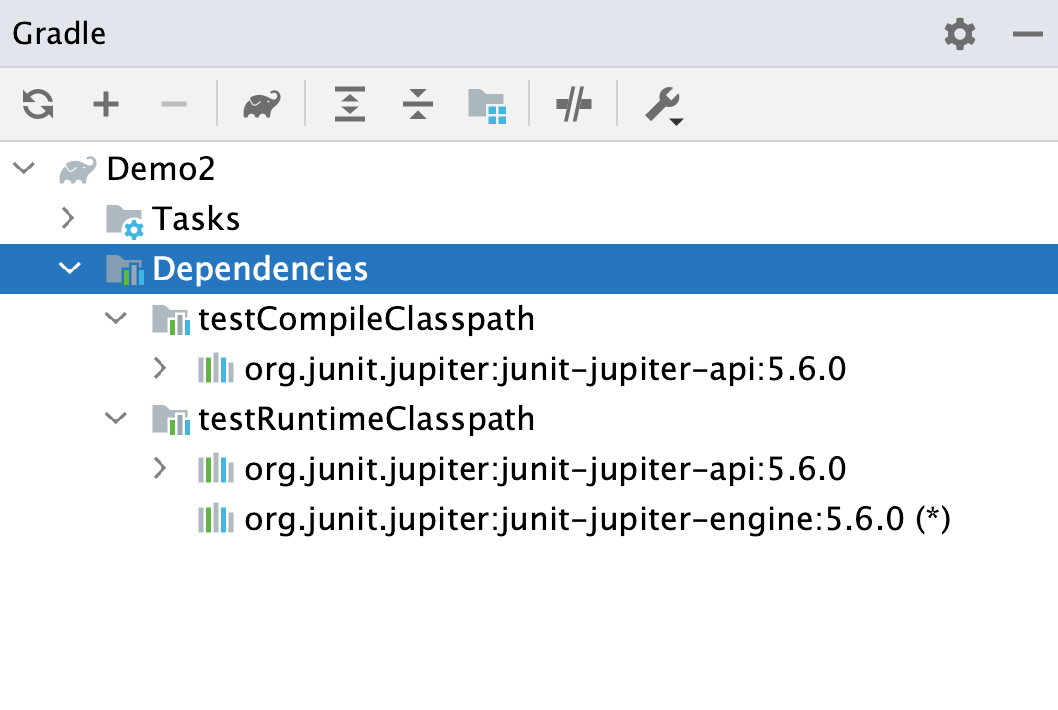
Add a custom source fix
-
Open the gradle.build file in the editor.
-
Declare a custom source set (In our example, it'south api).
sourceSets { api } dependencies { compile sourceSets.api.output }
(This source set contains interfaces without implementations. The implementations for the interfaces are in the default main source set.)
-
Open the Gradle tool window to see that IntelliJ IDEA added the
apicompile and runtime configurations.
The test source set contains the appropriate dependencies. Note that the default master source gear up has the compile dependency on the output of the api source set.
-
From the primary bill of fare, select File | Project Construction Ctrl+Alt+Shift+S to open the project structure. Notice that all source sets are represented as separate modules that are grouped into a single module. If yous click the test module and select the Dependencies tab, you will see a listing of dependencies for the source set.

Utilise source sets for custom tests
You lot can add together custom tests and run them separately from the main ones using a source prepare characteristic.
-
Declare a source set the same way as you would declare the custom source set. Besides the name of you source set up, specify an output directory and a task that volition run the declared test. For example, declare an integration test
integrationTest.sourceSets { integrationTest { java { srcDir 'src/integrationtest/java' } resources { srcDir 'src/integrationtest/resource' } compileClasspath += sourceSets.master.runtimeClasspath } } task integrationTest(type: Examination) { clarification = "Runs Integration Tests" testClassesDirs = sourceSets.integrationTest.output.classesDirs classpath += sourceSets.integrationTest.runtimeClasspath }
-
In the Gradle tool window, click .
-
In the list that opens, double-click the
integrationTestto run it.
Add parcel prefixes in the Gradle project
If you use parcel prefixes in your Gradle project, specify them in the build.gradle file. That way, everything is saved when you reimport your projection.
For more information, run across https://github.com/JetBrains/gradle-idea-ext-plugin.
-
Open the build.gradle file.
-
Add the following plugin to back up bundle prefixes:
plugins { id "org.jetbrains.gradle.plugin.idea-ext" version "0.5" }
-
Add the parcel prefixes. For case, you have the following set of source sets:
sourceSets { main.java.srcDirs = [] principal.java.srcDirs += "src" primary.java.srcDirs += "src/principal/coffee" main.java.srcDirs += "../other-root/src/principal/java" }
Add the package prefixes (in our instance it is "org.case") to them with the following code:
idea { module { settings { packagePrefix["src"] = "org.case" packagePrefix["src/primary/java"] = "org.instance" packagePrefix["../other-root/src/main/java"] = "org.case" } } }
-
Reimport your changes or use the auto-import.
Specify IDE-specific settings in the build.gradle file
Using the gradle-thought-ext plugin, y'all can describe project settings such as project encodings, and the encoding for backdrop files inside the build.gradle file.
-
Open the build.gradle file.
-
Add together the following plugin to support the encodings configuration:
plugins { id "org.jetbrains.gradle.plugin.idea-ext" version "0.5" }
-
Describe the project encodings with the following code:
import org.jetbrains.gradle.ext.EncodingConfiguration.BomPolicy idea { projection { settings { encodings { encoding = 'windows-1251' bomPolicy = BomPolicy.WITH_NO_BOM properties { encoding = '<System Default>' transparentNativeToAsciiConversion = false } mapping['../sample-gradle-gratis/module'] = 'windows-1251' mapping['module'] = 'windows-1251' mapping['module2/src/main/java'] = 'windows-1251' } } } }
-
Reimport your changes or use the auto-import.
Utilize buildSrc
If you have a large Gradle script that includes several Coffee, Groovy, or Kotlin classes, you can move such classes to the buildSrc directory and refer to them from your main Gradle script. In this case you ensure the readability of the build.gradle file.
-
If you don't have and existing
buildSrc, add it every bit a Gradle module to your main project.
-
Open your main build.gradle file in the editor and move the classes you need to the main subdirectory of the buildSrc directory.

-
Run your job from your project'south build.gradle file.

Configure the build and run actions
By default, IntelliJ IDEA uses Gradle for building and running projects.
When you build a project (), IntelliJ Idea invokes the corresponding tasks using Gradle. Gradle besides executes the Run and Debug actions from the menu. HotSwap is as well gets triggered and the classes are reloaded during a debugging process.
If you have linked projects, you lot can configure how to build each linked project.
-
In the Settings/Preferences dialog (Ctrl+Alt+Southward), go to .
-
On the Gradle settings page, in the Gradle Projects department, select a Gradle project you need.
-
In the Build and run using list, select the appropriate option and click OK to save the changes.
If y'all want to use IntelliJ Thought for edifice a Gradle project, you need to explicitly specify and then.
Consul a build to IntelliJ IDEA
It might be helpful to use IntelliJ IDEA for edifice a pure Java or Kotlin project. Information technology could speed up the building process since IntelliJ Idea supports the incremental build. Still, proceed in heed that the IntelliJ IDEA compiler does non support some parts of the Gradle projection build processing and might crusade problems in building your projection correctly.
-
Click
in the Gradle tool window.
Alternatively, in the Settings/Preferences dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S), become to .
-
On the Gradle page, from the Build and run using listing, select Intellij IDEA.

Note that the Run test using option stays agile, and you can select how you want to run your tests even if you lot delegated all build and run actions to IntelliJ IDEA.
-
Click OK.
Now if you build your Gradle project, it volition be built with IntelliJ IDEA.
Last modified: 20 Oct 2021
Source: https://www.jetbrains.com/help/idea/work-with-gradle-projects.html
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Please Re Import the Gradle Project and Try Again"
Posting Komentar