Reading Guide 18.1 How Economic Systems Work
Always wondered how the local, national or global economy works? We take a wait at some of the fundamental definitions and principles of economics, as well equally different types of economies.

Whether information technology'south thriving or in refuse, the global and local economy is rarely out of the news. Only what, exactly, do these terms mean? And how does an economy piece of work? Nosotros explore the basic principles of economics, exploring how they affect the world around united states of america and how nosotros influence them.
Every bit well as looking at some of the key terms and concepts related to the economy, we also examine some of the dissimilar types of economic systems and types of economies. Finally, we'll explore how an economy works.
A definition of key terms
Let's beginning by exploring some terms that are going to crop up throughout the article. These unproblematic definitions can be a useful reference:
- Boom and bust . Also known as the business organisation bicycle, this refers to the economic pattern of growth followed by recession.
- Budget . The yearly outline for public spending and taxation in a item country.
- Capital . Essentially, upper-case letter refers to either money or avails that are used in the economy.
- Debt . A primal role of economic growth, debt allows the government, companies and individuals to brand investments they wouldn't otherwise be able to afford.
- Economy . An economy is a circuitous web of production and consumption that determines how resource and capital are allocated.
- Economics . The study of how a society uses resources.
- Financial system . The institutions and organisations that facilitate the movement of money in an economy.
- Gdp . Gross domestic production, the total value of a country's finished goods and services in a specific time flow.
- Globalisation . The tendency towards interconnectedness around the world. Often meaning that appurtenances, services and resources are made accessible to a global audience .
- Growth . The increment in the goods and services produced per capita in an economy over a period of time.
- Aggrandizement . The wholesale ascension of prices across an economy. Usually expressed every bit an annual percentage change. It unremarkably ways the decrease in purchasing power of a currency.
- Macroeconomics . The big picture assay of the economy, including trends in inflation, growth, and similar factors.
- Microeconomics. The finer-detail analysis of the economic system, including how households and businesses brand financial decisions.
- Recession . A menstruation of negative economic growth, sometimes measured equally a sustained period of falling Gdp.
- Stock market . An interconnected organisation of businesses, investors, and securities, where people buy and sell shares in companies.
What is an economy? A brief summary
Earlier we look at how the economy works, let'south first explore the term in more detail. As you might expect, it'due south a fairly complex concept with many different elements. Equally this is an introductory article, we'll keep things unproblematic. However, if you want to learn about the economic system in more particular, we've provided links to courses and resources that can assist you.
You can likewise check out the video from our open step; what is an economy?
First, let'south explore the dissimilar levels of complexity when information technology comes to an economy:
Local economies
When we think most a local economy, we're referring to the interconnected markets and networks within a particular community. The local government, organisations, businesses, and people all contribute to this economy.
Local businesses may purchase their raw materials from sellers who are nearby. These sellers may get grants or tax relief from local councils or governments. People in the area pay tax, work for businesses, and buy goods and services.
Of form, historically, such local economies were fairly commonplace. As nosotros explore in our open step on globalisation , until the beginning in the 19th Century, consumption and production normally happened in the same place. Food was grown locally, and those in the surrounding area purchased it, for example.
However, as countries, and eventually the unabridged world, became more accessible and connected, economic webs expanded to go ever more complex. Of form, local economies still exist; they're just part of something larger.
National economies
According to the Banking concern of England, when nosotros talk of a national economic system, such as the United kingdom of great britain and northern ireland economy, we're referring to a organisation for distributing scarce resource. An economy, they propose, is based on the fact that resource, such equally workers, country and raw materials, are limited. Need, all the same, is infinite.
Although this principle of distributing deficient resources is at the heart of any economy, national governments often accept radically dissimilar approaches to how they mould and manufacture a nation's economy. That'due south why the Usa economy, for example, is very dissimilar from the Chinese economy.
By the time we could move resources and produce across borders, these national economies once more became office of a much wider network of interconnected nations.
The global economy
The world economy (besides known every bit the global economy ) refers to the economy of all humans of the globe. This definition includes the various economic systems and activities that take place within and between nations.
This broad scope captures the substitution of capital (money and assets) equally well equally the consumption and product of appurtenances. Thanks to globalisation, international trade, finance and investment all help to ability the earth's economic system.
Types of economic systems
Then far, we've spoken mainly in general terms. We've looked at how economies in general function. However, there are all kinds of unlike economical systems that local and national economies might adopt. What's more, throughout history, we've seen various types of systems emerge, thrive, and decline.
Below, we've briefly explored some of the main types of economic systems that have been used and are used today:
Bullwork
This blazon of economic organisation was used in the Centre Ages. Essentially a rex or ruler 'owned' all of the lands in a particular area. That ruler would and then allocate state to sure nobles who fought for them. Regular people worked the nobles' land, paying tax past means of products and services (such as food and farming) in commutation for protection.
Capitalism
Most economies around the world today follow a capitalist organization. Ane of the primal characteristics of a backer economy is that individual entities (every bit opposed to state-owned) command property and production in accord with their interests. In capitalism, supply and demand mean that market prices can be set to serve the interest of the wider society.
Another stand up-out characteristic of a capitalist economic system is that there is a motivation to make a profit. Examples of capitalist economies include the US, Uk, and Commonwealth of australia.
Socialism
While in capitalism, individual companies ain the means of production, in socialism, everything is owned by the country or the public. Rather than working for the profit of the individual, everyone works for wealth that is distributed amongst the people.
Rather than supply and demand setting prices and the production of goods, in a socialist economy, products and services are produced based on usage value – the needs of order. Examples of socialist economies include North Korea and The Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka.
Communism
Much like with socialism, a communist economy aims for ownership of the means of production by the customs. It aims to create a classless society where everyone contributes and takes out according to their ability and needs. Still, this often comes at the expense of individual freedoms.
Examples of communist countries today include China, Cuba and Vietnam. However, as we explore in our open step, countries can be both capitalist and communist .
Types of economies
Although the different types of economical systems outlined to a higher place be, it's rarely every bit rigid equally that. As we explore in our open step on unlike types of economies , the economy and markets are dependent on how they allocate the factors of production to control the economic system.
Markets are the mechanisms past which scarce resources are allocated. They ensure that consumers and producers can obtain the goods and services they desire. When it comes to macroeconomics, the type of marketplace a state has plays a big function in its economy.
There are ii extremes hither, depending on how much influence a government has over the market. As you'll observe throughout this article, politics and economics are closely linked subjects. With that in listen, there are three dissimilar types of economy at the macro level:
Command markets
At this extreme, all the factors of production are controlled by the state. This means:
- What to produce is determined by government preferences
- How to produce is determined by the authorities and their employees
- For whom to produce is determined past regime preferences
Free markets
At the other end of the spectrum are gratis-market economies. Rather than the authorities controlling decisions, the factors of production are decided by the consumer and producer and usually depend on coin. This ways:
- What to produce is determined by consumers' preferences
- How to produce is determined by producers seeking profit
- For whom to produce is adamant by purchasing power
Mixed markets
At the center of the spectrum is a mixed marketplace – a compromise between the other extremes. This means that in that location is some level of government intervention, unremarkably setting boundaries in which the complimentary market tin can operate. This ways:
- What to produce is adamant by consumers' preferences and partly past the government.
- How to produce is determined past producers seeking profits and partly by the regime.
- For whom to produce is determined by purchasing power and partly past government preferences.
Other types of economies
As we've seen, there are different levels at which economies operate. Whether at a local, national or international level, the mode we organise our markets and distribute resource tin vary considerably. That's why you'll often come across different phrases related to the economy. Here are some other notable types that you might encounter:
- Green economy . An economy with the aim of developing sustainably without damaging the environment. Ofttimes, this means the economic system is focused on being low-carbon, using resource efficiently , and is socially inclusive.
- Digital economy . An economy based on computers and the internet. In the modern world, the digital economic system is increasingly a part of the traditional economy. People and devices around the globe now form an interconnected web, where merchandise and commerce are possible at the press of a button.
- Gig economy . Another modern aspect of the wider economy is the gig economy. Hither, the labour market is made up of freelancers and brusk-term contracts rather than permanent jobs. Information technology gives flexibility to employers and employees, but it can brand career progression more difficult.
How does the economic system work?
A key part of understanding how an economy works is to empathise what underpins information technology and the principles that drive information technology. We've explored the nuts of both of these points to a higher place, pregnant nosotros tin now look at the mode an economy forms and works and the factors that bear upon and are impacted by information technology.
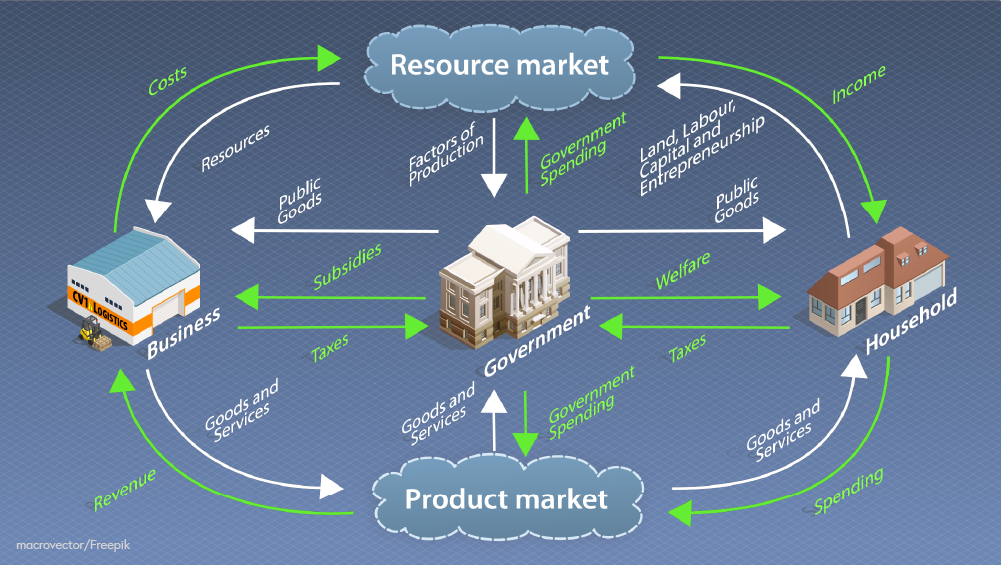 Click here to expand the image
Click here to expand the image
Again, this is a summit-level view. If you want to learn more than well-nigh economics, you can check out our range of online economic science courses .
How an economic system forms
As divers on the financial website Investopedia, an economy is formed whenever a group of people combine their skills, interests, and desire to trade with others. Essentially, when people get-go to merchandise considering they think information technology will make them better off, an economic market forms.
As we saw in our video above, households, businesses, and governments, along with the resources market place and product marketplace, form the basis of an economy.
Macroeconomics and microeconomics
When thinking nearly the economic system from an economics perspective, in that location are two sides to consider – macroeconomics and microeconomics.
Co-ordinate to the IMF , macroeconomics focuses on the 'big pic' of the economy, such as the employment rate, gross domestic production (GDP), and inflation rates. These are the factors that a nation'south regime creates financial policies in relation to.
Microeconomics looks at the more granular detail of an economy. They explore how households and businesses make financial decisions related to factors such as the impact of supply and demand on a market.
Both micro and macro factors influence the fashion an economy works, showing just how much complication there is in this expanse.
The forces that impact an economic system (economic indicators)
Then, an economy works by creating a network of markets composed of buyers and sellers. These economical markets allocate scarce resources amidst the players within that market. When we call back of a country'southward economy, we're usually thinking in terms of macroeconomics . Similarly, when we're thinking of the private markets in the network, we call up in terms of microeconomics.
So what determines how well or poorly an economy performs? Equally nosotros explore in our open up step on economical factors , some of the aspects that influence an economy include growth, unemployment rates, inflation, interest and substitution rates, and commodity (oil, steel, gold, etc) prices. These factors touch the income and purchasing power of households and organisations.
When nosotros measure the success of a national economy, we talk in terms of gdp – the value of the land's finished goods and services in a specific fourth dimension period.
The impacts of an economy
We've learned that the economy is all effectually us and that we all play a part in it. But how does the economic system affect our day-to-twenty-four hour period life? Every bit you might expect, there are several factors to consider here. We've outlined just a few of them below:
- Living costs . The cost of living is tied closely to the economy. It's defined equally the amount of money needed to cover basic expenses such every bit food, housing and taxes. This cost is measured by the inflation rate. As goods and services cost more than, the power of a unit of currency lessens.
- Employment rates . A booming economy will also hateful that rates of employment increase. As more goods and services (resources) are in demand, more people are needed to provide them, creating more jobs. The same is true of the opposite – when demand is depression, there are fewer jobs available.
- Government spending . The performance of a country's economy volition impact the policies and spending of the government. As businesses brand more than money and pay more than tax, there is improved cash flow, allowing the government to invest in infrastructure and services.
- Quality of life . As a country's economy grows, there are more resources available to spend on sectors such as education and healthcare. What's more than, information technology means there are more jobs available, a reduction in poverty, and overall improved wellbeing for the people in that economy. At least, in theory.
Again, this is a fairly simplified explanation of these points. In reality, there are many complexities and mechanisms that decide the economical impacts on individuals, organisations and nations. It's linked to the way societies abound and develop, and can be a force for change.
As Guilherme Winspear, Head of Marketing at fintech visitor Pockit highlights:
"The economic system is in constant evolution and the digital revolution of the by decades accept inspired a number of companies to address various consumer needs and drive inclusion."
He also outlines the fact that tech companies can bear upon both the local and global economies. Whether information technology's through access to education or providing innovative banking services, technology can be transformative.
Final thoughts
So how does an economy work? Well, it'due south complicated. All the same, in essence, economies piece of work by distributing scarce resource amid individuals and entities. A series of markets where appurtenances and services are exchanged, facilitated past capital, combine to make an economy. These networks be at a local, national and international level.
Economies tin can take many different forms, focus on various priorities, and have dissimilar levels of government intervention. On both a micro and macro level, there are factors that determine how well or desperately an economy performs. Similarly, our lives are affected by the diverse ebbs and flows of the systems we're a part of.
Learning well-nigh the economy can encourage y'all to empathize the various forces that impact it. At FutureLearn, we accept diverse courses that tin assist you acquire about the economic system.
Source: https://www.futurelearn.com/info/blog/how-does-the-economy-work
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Reading Guide 18.1 How Economic Systems Work"
Posting Komentar